What is AEPS Service?
The Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS) is a transformative digital banking initiative in India. It enables financial services for everyone—especially in rural and underserved areas—by using Aadhaar authentication and biometric verification. AEPS allows users to conduct secure banking transactions without needing debit/credit cards or smartphones.
It is a key pillar of India’s digital financial inclusion and is revolutionizing banking accessibility across the country.
What is AEPS?
AEPS (Aadhaar Enabled Payment System) is a secure and interoperable platform that allows users to perform financial transactions using their:
- Aadhaar number
- Biometric authentication (fingerprint or iris scan)
AEPS eliminates the need for physical banking tools like ATM cards or passbooks and operates through micro-ATMs and banking correspondents (BCs).
It was developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) to offer banking access even in areas lacking physical branches.
How AEPS Works
AEPS operates on a bank-led model and primarily uses micro-ATMs or Point of Sale (POS) terminals, managed by business correspondents or local agents.
AEPS Transaction Flow:
-
User visits an AEPS-enabled outlet or banking correspondent.
-
User provides their Aadhaar number and selects a service:
- Cash withdrawal
- Deposit
- Balance inquiry
- Fund transfer
- Mini statement
-
Biometric authentication is used (typically fingerprint or iris scan).
-
On successful verification, the transaction is processed in real time, and a receipt is generated.
💡 No bank account details or physical cards are needed—only an Aadhaar-linked account and biometric verification.
Key Features and Benefits
1. Financial Inclusion
- Bridges the urban-rural banking divide.
- Supports schemes like PM Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) and Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) to ensure benefits reach the right recipients.
2. Secure and Convenient
- Transactions are secured through biometric authentication.
- Services available 24/7 at AEPS-enabled outlets.
3. Interoperability
- Works across all participating banks.
- Users can access their Aadhaar-linked account regardless of their bank.
4. Cost-Effective
- Reduces banking operational costs.
- Micro-ATMs are low-cost and easy to install.
5. No Need for Technology or Cards
- No smartphones, internet, or debit/credit cards required—just Aadhaar and biometrics.
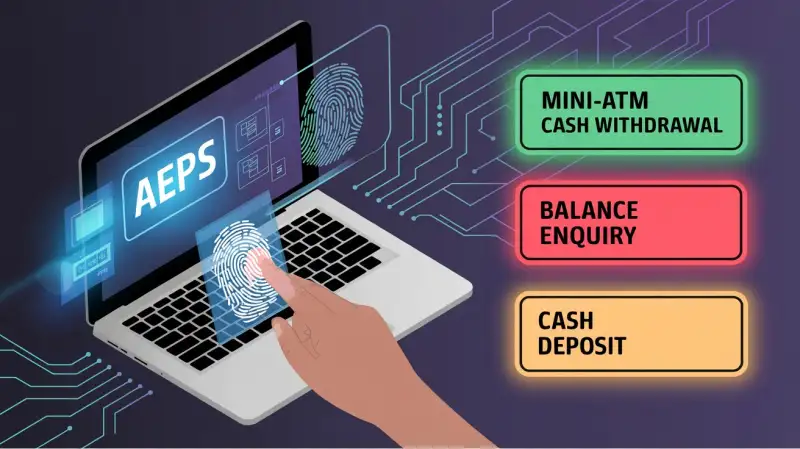
Services Offered Through AEPS
- Cash Withdrawal
- Cash Deposit
- Balance Inquiry
- Mini Statement
- Aadhaar-to-Aadhaar Fund Transfer
AEPS Usage and Growth: Key Statistics
- Transaction Volume (Aug 2024): 100 million
- Transaction Value (Aug 2024): ₹24,676 crore
- Average Daily Transactions: 3.21 million (₹796 crore/day)
- Annual (April 2024): 187.21 million OFF-US transactions worth ₹24,608.43 crore
- User Base (2023): Over 370 million
- Growth Trend: AEPS usage grew by 11% from May to Aug 2024
- Bank Participation: Over 150 banks (public, cooperative, small finance)
Challenges and Limitations
1. Transaction Failures
- 34% failure rate (2023) due to biometric mismatches or network issues.
2. Fraud and Security Risks
- Rising fraud led banks to limit services or enforce stricter verification.
3. Accessibility Concerns
- Elderly and physically challenged may face difficulties with biometric systems.
4. Volume Decline
- April 2024: AEPS volume dropped to 94 million from 118 million in March.
- Year-on-year: 7% drop in volume, 15% in transaction value.
Regulatory and Security Measures
To improve safety and efficiency:
-
RBI enforced stricter onboarding and KYC norms.
-
Real-time fraud monitoring in place.
-
Work underway on:
- Additional authentication layers
- Better biometric hardware and quality
The Future of AEPS in India
AEPS will continue to play a pivotal role in India’s digital transformation. Upcoming innovations include:
- Voice-based verification
- Offline AEPS transactions
- QR code integration
- Enhanced biometrics
Conclusion
AEPS has revolutionized banking for millions by offering secure, affordable, and inclusive access to financial services using Aadhaar and biometrics.
Though it faces challenges like transaction failures and biometric issues, regulatory bodies are actively improving the system. AEPS is more than just a payment method—it’s a cornerstone of digital empowerment and financial inclusion in India.


